14. Endpoints & REST APIs
Production Environment and the Endpoint
When we discussed the production environment , the endpoint was defined as the interface to the model. This interface ( endpoint ) facilitates an ease of communication between the model and the application . Specifically, this interface ( endpoint )
- Allows the application to send user data to the model and
- Receives predictions back from the model based upon that user data .
Model, Application, and Endpoint

One way to think of the endpoint that acts as this interface , is to think of a Python program where:
- the endpoint itself is like a function call
- the function itself would be the model and
- the Python program is the application .
The image above depicts the association between a Python program and the endpoint , model , and application .
- the endpoint : line 8 function call to ml_model
- the model : beginning on line 14 function definition for ml_model
- the application : Python program web_app.py
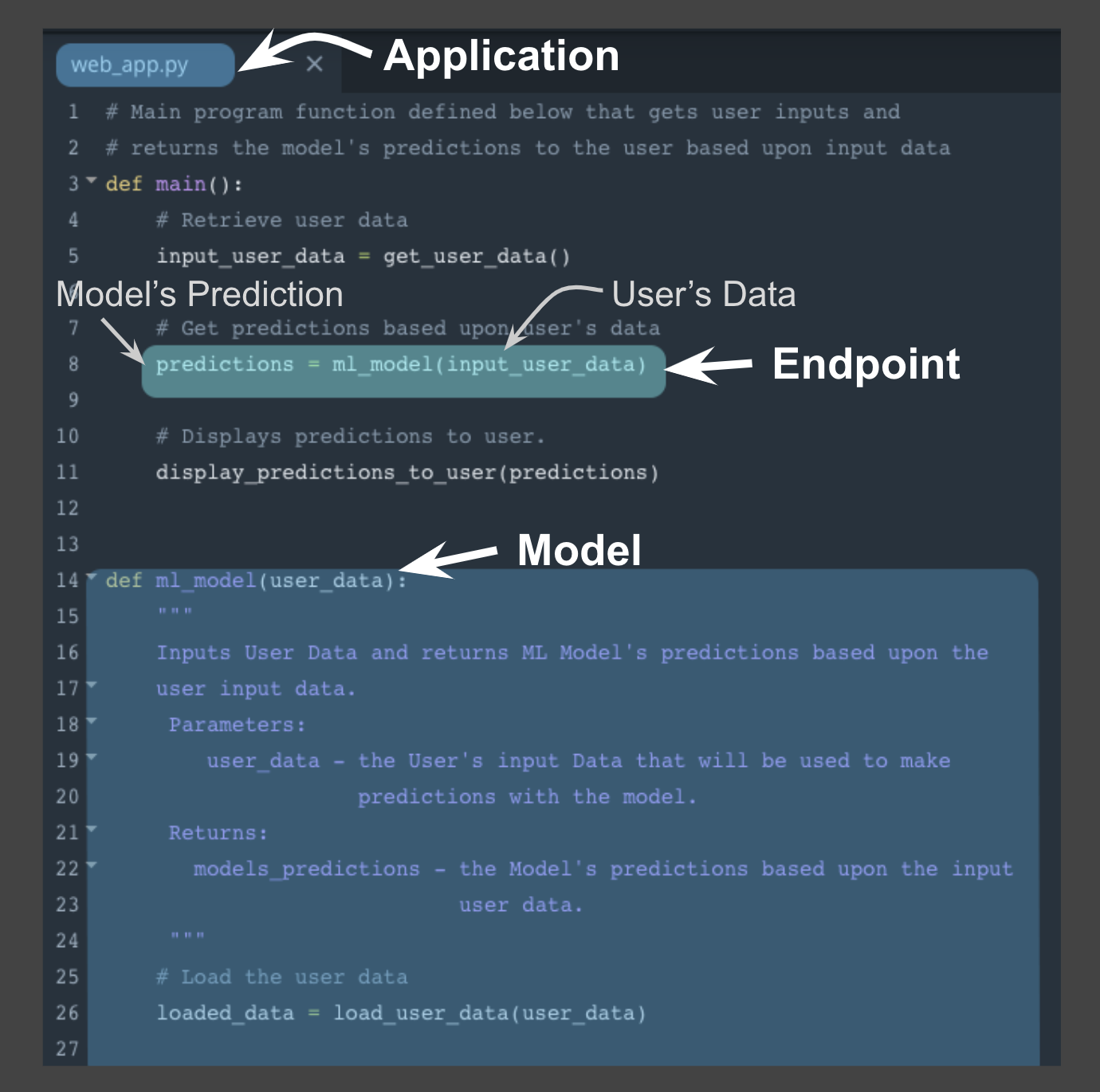
Using this example above notice the following:
-
Similar to a function call the endpoint accepts user data as the input and returns the model’s prediction based upon this input through the endpoint .
-
In the example, the user data is the input argument and the prediction is the returned value from the function call .
-
The application , here the python program , displays the model’s prediction to the application user .
This example highlights how the endpoint itself is just the interface between the model and the application ; where this interface enables users to get predictions from the deployed model based on their user data .
Next we'll focus on how the endpoint ( interface ) facilitates communication between application and model .
Endpoint and REST API
Communication between the application and the model is done through the endpoint ( interface ), where the endpoint is an Application Programming Interface ( API ).
-
An easy way to think of an API , is as a set of rules that enable programs, here the application and the model , to communicate with each other.
-
In this case, our API uses a RE presentational S tate T ransfer, REST , architecture that provides a framework for the set of rules and constraints that must be adhered to for communication between programs.
-
This REST API is one that uses HTTP requests and responses to enable communication between the application and the model through the endpoint ( interface ).
-
Noting that both the HTTP request and HTTP response are communications sent between the application and model .
The HTTP request that’s sent from your application to your model is composed of four parts:
-
Endpoint
- This endpoint will be in the form of a URL, Uniform Resource Locator, which is commonly known as a web address.
-
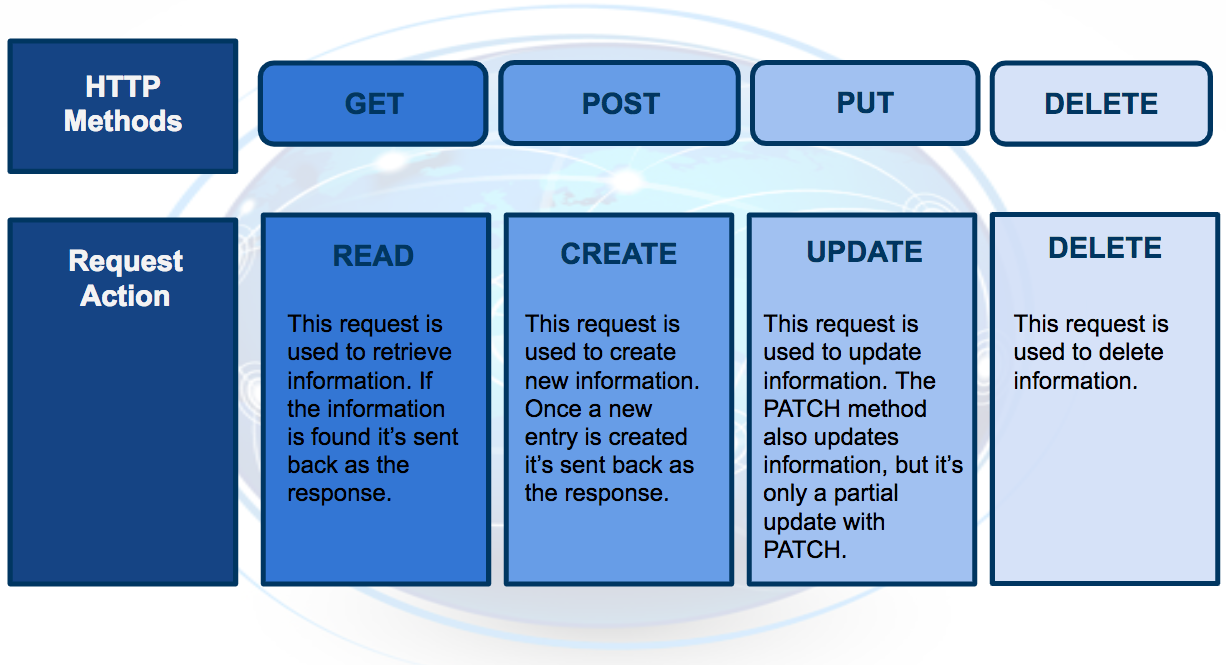
HTTP Method
- Below you will find four of the HTTP methods , but for purposes of deployment our application will use the POST method only .
-
HTTP Headers
- The headers will contain additional information, like the format of the data within the message, that’s passed to the receiving program.
-
Message (Data or Body)
- The final part is the message (data or body); for deployment will contain the user’s data which is input into the model .
The HTTP response sent from your model to your application is composed of three parts:
-
HTTP Status Code
- If the model successfully received and processed the user’s data that was sent in the message , the status code should start with a 2 , like 200 .
-
HTTP Headers
- The headers will contain additional information, like the format of the data within the message , that’s passed to the receiving program.
-
Message (Data or Body)
- What’s returned as the data within the message is the prediction that’s provided by the model .
This prediction is then presented to the application user through the application . The endpoint is the interface that enables communication between the application and the model using a REST API .
As we learn more about REST*ful *API , realize that it's the application’s responsibility:
- To format the user’s data in a way that can be easily put into the HTTP request message and used by the model .
- To translate the predictions from the HTTP response message in a way that’s easy for the application user’s to understand.
Notice the following regarding the information included in the HTTP messages sent between application and model :
- Often user's data will need to be in a CSV or JSON format with a specific ordering of the data that's dependent upon the model used.
- Often predictions will be returned in CSV or JSON format with a specific ordering of the returned predictions dependent upon the model used.